Basic troubleshooting with Windows CMD command.
.png)
The Windows operating system contains numerous built-in, command line networking utilities. These tools range from the obscure to the commonplace. However, there are some built-in networking tools that Windows IT Administrator should be familiar with.
1. Ping
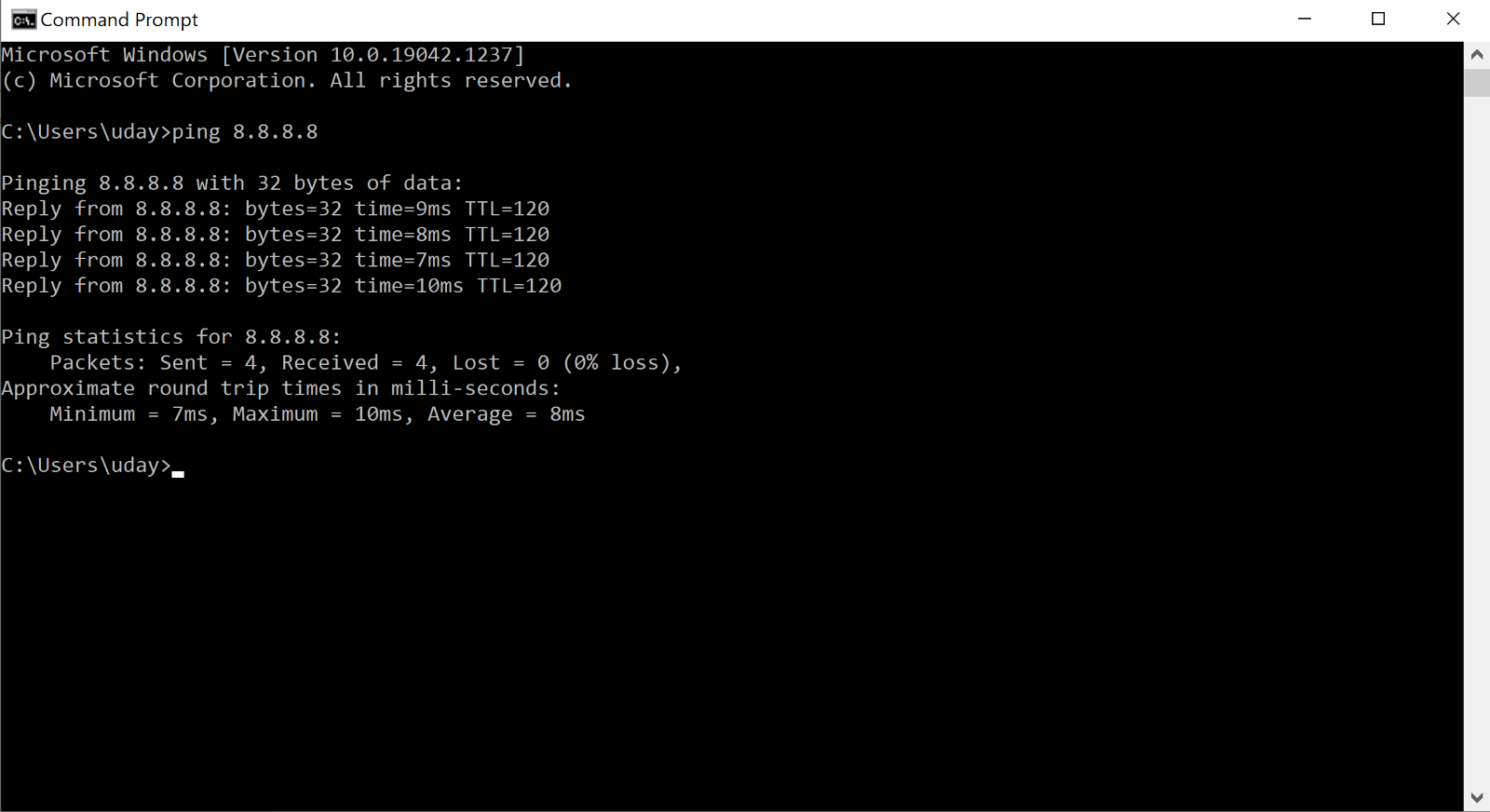
Ping is used to test the ability of one network host to communicate with another. Simply enter the Ping command, followed by the name or the IP address of the destination host. Assuming that there are no network problems or firewalls preventing the ping from completing, the remote host will respond to the ping with four packets. Receiving these packets confirms that a valid and functional network path exists between the two hosts.
Type: PING 192.168.45.1
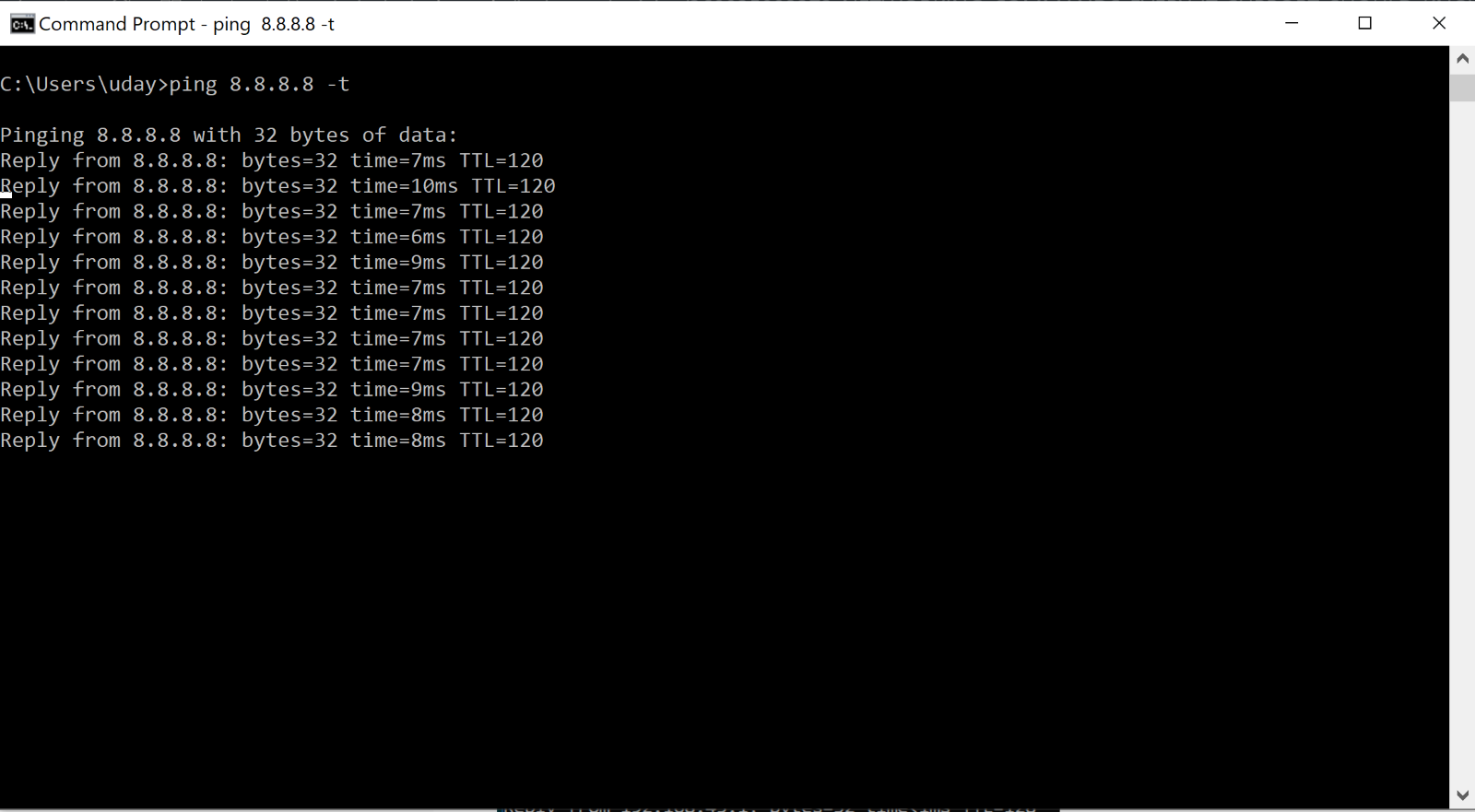
Type: PING 192.168.45.1 -t ( for continues packet receiving ) and CTR+C to stop
2. ARP
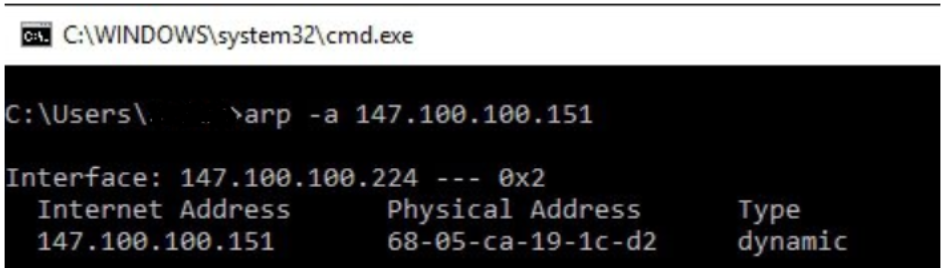
The ARP command corresponds to the Address Resolution Protocol. Although it is easy to think of network communications in terms of IP addressing, packet delivery is ultimately dependent on the Media Access Control (MAC) address of the device’s network adapter. This is where the Address Resolution Protocol comes into play. Its job is to map IP addresses to MAC addresses.
Windows devices maintain an ARP cache, which contains the results of recent ARP queries. You can see the contents of this cache by using the ARP -A command. If you are having problems communicating with one specific host, you can append the remote host’s IP address to the ARP -A command.
3. Tracert
Functionally, Tracert works similarly to Ping. The major difference is that Tracert sends a series of ICMP echo requests, and the request’s TTL increased by 1 each time. This allows the utility to display the routers through which packets are passing to be identified. When possible, Windows displays the duration and IP address or fully qualified domain name of each hop.
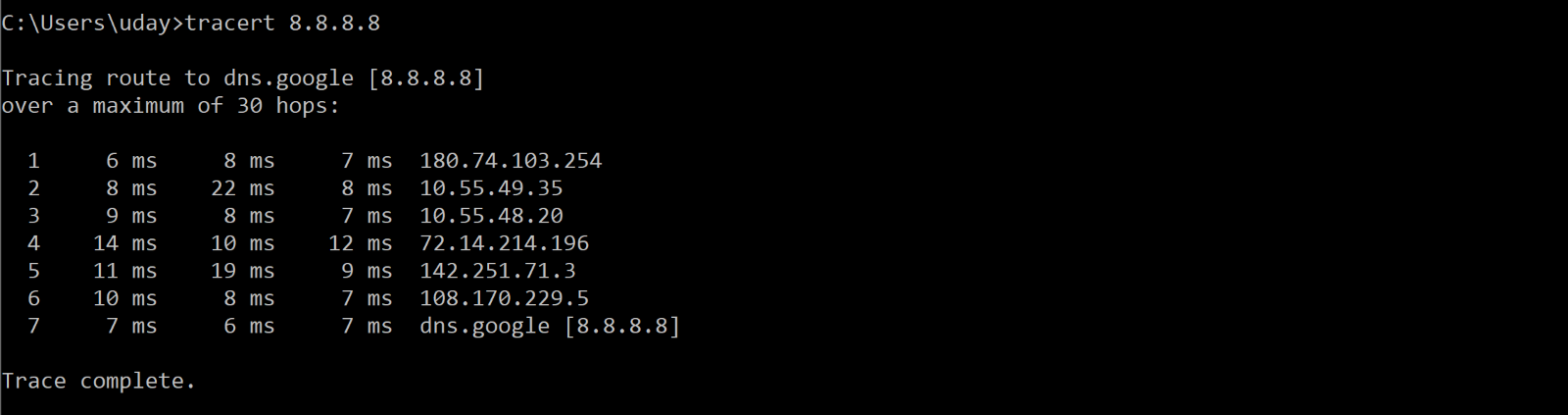
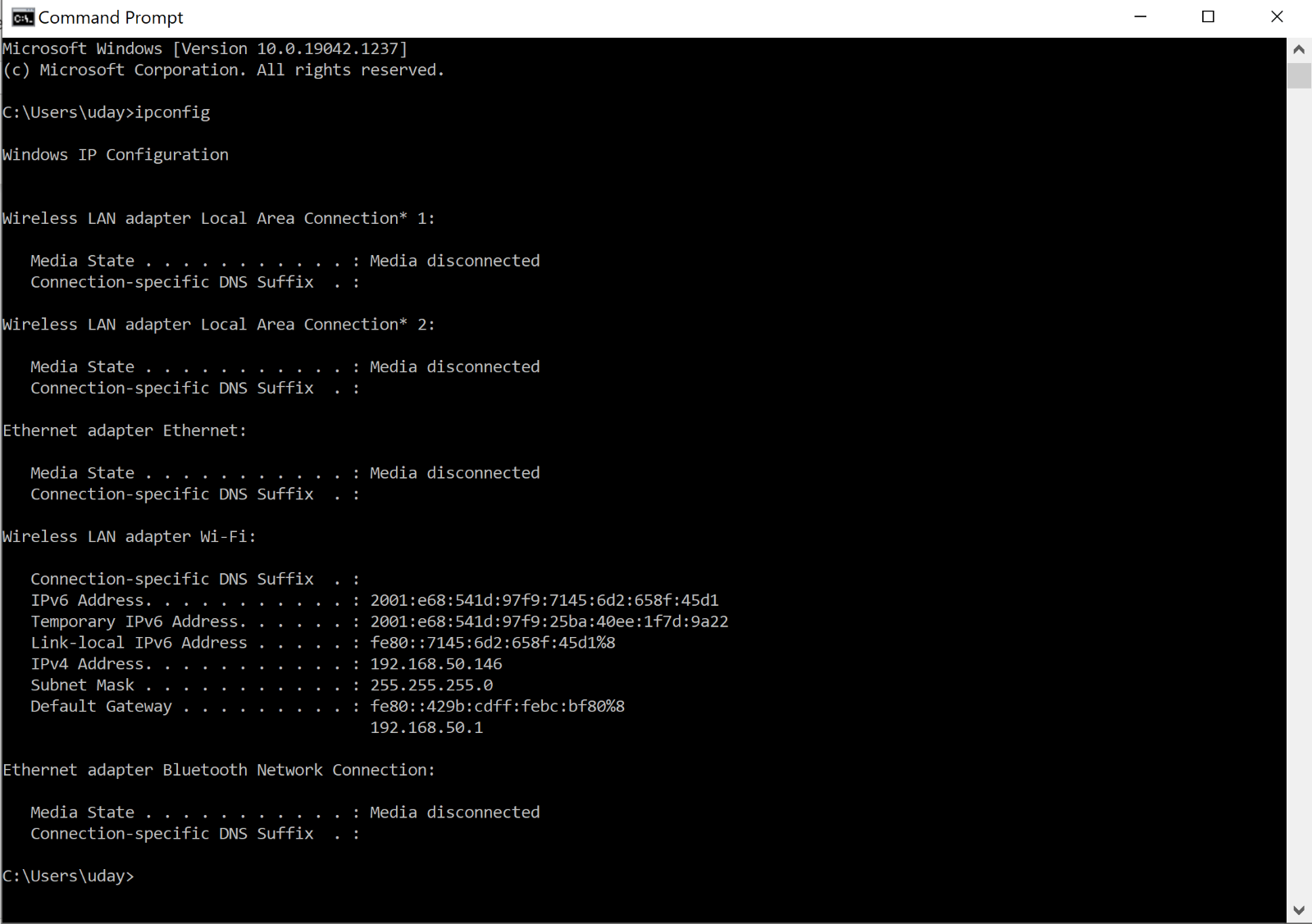
4. IpConfig
The IPConfig command will display basic IP address configuration information for the device. Simply type IPConfig at the Windows command prompt, and you will be presented with the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway that the device is currently using.
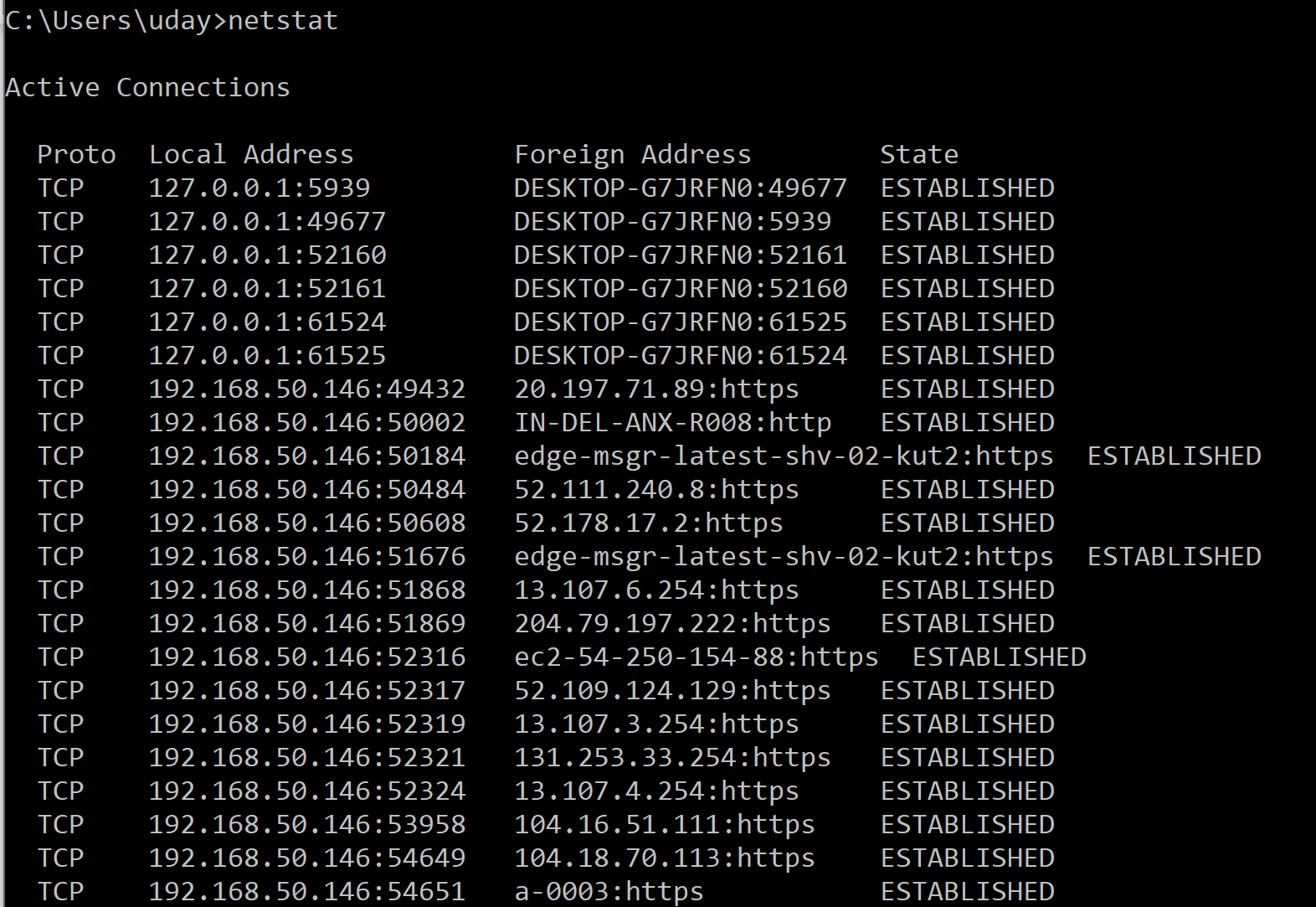
5. NetStat
If you are experiencing problems with network communications, then network statistics can sometimes help point you toward the root cause of the problem. That’s where the aptly named NetStat command comes into play. This command has a number of different functions, but the most useful of these is to display network summary information for the device. To see this type of summary information, just type NetStat -e.
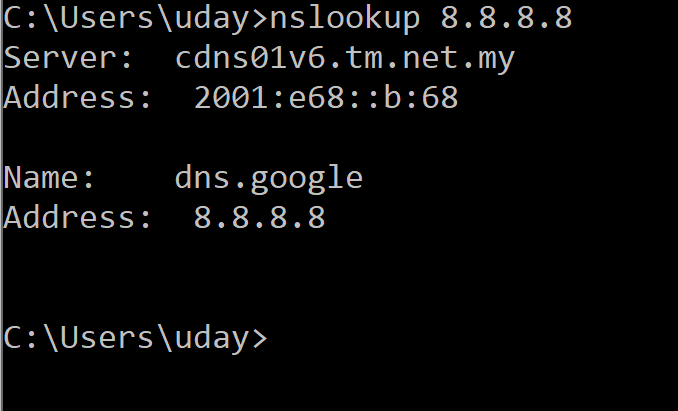
6. NSLookup
NSLookup is a great utility for diagnosing DNS name resolution problems. Just type the NSLookup command, and Windows will display the name and IP address of the device’s default DNS server. From there, you can type host names in an effort to see if the DNS server is able to resolve the specified host name.